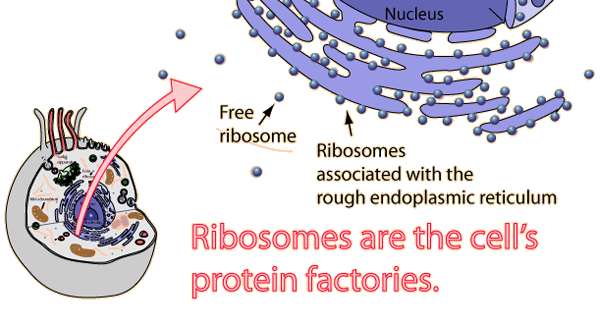
Ribosomes were first discovered by Robinson and Brown (1953) in plant cell and by Palade (1955) in animal cell. Palade also named these as ribonucleo-protein particles. atherefore, Ribosomes are naked ribonucleoprotein protoplasmic particles which functions as the sites of protein and polypeptide synthesis. Ribosomes are also called Protein Factories. These are spherical microscopic bodies found in all living cells except mammalian red blood corpuscles.
Ribosomes in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are differ in their RNA and protein molecules. Each ribosomes consists of two unequal subunits, larger and smaller subunit. The smaller subunit fits over a larger subunit as a cap. The two subunits usually lies freely in the cytoplasm of the cell but both subunits will get associate at the time of polypeptide synthesis and Mg ions are required for this association.
Ribosomes may occur singly are called monosomes but during protein synthesis number of ribosomes participated or in other words when there is synthesis of number of same type of polypeptides over ribosomes then they are interconnected by strand of mRNA and collectively are known as the Polyribosomes. Ribosomes are present in cytoplasm of the cell and in the organelles. The organelle ribosomes are present in the plastids and mitochondria. Because of the presence of their own ribosomes and DNA these organelle are able to synthesis some types of proteins. Therefore, these organelles are also called semi-autonomous organelles. The cytoplasmic ribosome may be free or attached to the ER. Different types of ribosomes are involved in the synthesis of different types of proteins e.g. structural proteins from free ribosomes and globular proteins from robosomes bound to ER.
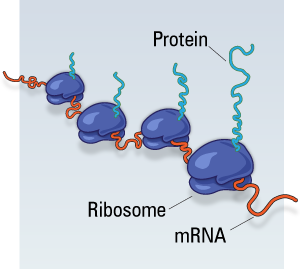
Polyribosome
The size of the ribosomes is determined by sedimentation coefficient in the centrifuge. Two types of ribosomes are found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells on the basis of their sedimentation coefficient. In eukaryotic cells the nature of ribosome is 80S and it has two sununits larger 60S and smaller 40S likewise prokaryotic cells have 70S ribosomes and they have larger subunit 50S and smaller 30S.
Chemically a ribosome is made up of two parts, proteins and rRNA. The principal site of the synthesis of ribosomal RNA is nucleolus region in the nucleus of the cell. The ribosomal proteins seem to be synthesized in the cytoplasm but migrated to the nucleoli for the formation of ribosomes.
Functions:- i) Ribosomes are the organelles involved the protein synthesis.
ii) Free ribosomes synthesise structural and enzymatic proteins for use inside the cell and attached ribosomes synthesise proteins for transport.
No comments:
Post a Comment