Stomata are the pores which takes part in the transpiration that means evaporation of water from these pores and also play important role in the gaseous exchange during photosynthesis and respiration. Stomatal movements are regulated by the change of turgor pressure in the guard cells or in other way stomata functions as turgor-operated valves. Guard cells will swell up by absorption of water and walls will stretch up with result of opening of stomata. Stomata generally opens during day time and closed during night time. The conditions required for the opening of stomata during day time are like light, high pH, low concentration of CO2 and availability of water. Likewise during night time stomata will close because of darkness, low pH, high CO2 concentration and dehydration. Mechanism of stomatal opening is described by three main theories :-
i) Hypothesis of guard cell photosynthesis:- This theory was given by Schwendener in 1881. According to this hypothesis guards cells have choroplast and during day time these chloroplast show photosynthesis as a result of photosynthesis sugar molecules produced. This sugar will increase the osmotic pressure inside the guard cells. Because of Osmotic pressure guard cells will start to absorb water from the near epidermal cells. Due to turgor pressure stomata will open. however the photosynthetic activities of guard cells are very less so this was not accepted very much.
ii) Classical starch hydrolysis theory:- This theory was spelled out by Sayre in 1923 and then modified by steward in 1964. According to this theory guard cells contain starch. during day time when CO2 concentration is low (in the day time because of photosynthesis the CO2 concentration is low) and the pH of the guard cell will increase then enzyme phosphorylase will become active then this enzyme converts the starch present in the guard cells to glucose 1-phosphate. Then glucose 1-phosphate will change into glucose 6-phosphate and latter this molecule after hydrolysis converts into glucose and phosphoric acid.
phosphorylase
Starch + nH3PO4 = n Glucose 1-phosphate
phosphoglucomutase
Glucose 1-phosphate = Glucose 6-phosphate
phosphatase
Glucose 6-phosphate + water = Glucose + H3PO4
Glucose increases osmotic pressure of the guard cells and guard cells will start to absorb water from the adjacent cells and stomata will open. During night time reverse reaction will take place and due to formation of starch the osmotic concentration of guard cells will decrease and guard cells with loss of water will shrink and then closed. But this was not accepted because
i) Glucose is not found in the guard cells at the time of stomatal opening.
ii) The starch and glucose conversion is usually slow reaction but stomatal movements are rapid.
iii) Malate or K+ ion Pump Hypothesis:- This theory was put forward by Steward in 1974. This theory explains that during day time the pH of the guard cell increases due to absorption of H+ ion concentration in the guard cell. CO2 concentration is less due to its assimilation by mesophyll cells. An increase in pH causes the hydrolysis of starch into organic acids.
Starch --- Hexose Phosphate --- Phosphoglyceric acid --- Phosphoenol Pyruvate
Phosphoenol pyruvate is also the intermediate product of respiratory pathway. So with the help of PEP carboxylase the phosphoenol pyruvate will combine with CO2 forms oxalic acid. Latter this organic acid gets changed into malic acid. Malic acid dissociates into malate and H+ ions. H+ ions will pass out from the guard cells with the exchange of K+ ions. These ions and malate ions will increases the osmotic pressure inside the vacuoles of guard cells and as a result water gets absorbed by the guard cells and stomata will open. In the dark reverse reaction taks place and stomata will closed.
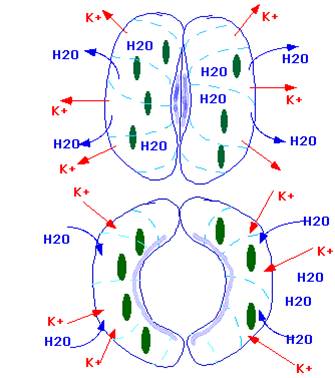
Role of K+ ions in Opening and Closing of Stomata
i) Hypothesis of guard cell photosynthesis:- This theory was given by Schwendener in 1881. According to this hypothesis guards cells have choroplast and during day time these chloroplast show photosynthesis as a result of photosynthesis sugar molecules produced. This sugar will increase the osmotic pressure inside the guard cells. Because of Osmotic pressure guard cells will start to absorb water from the near epidermal cells. Due to turgor pressure stomata will open. however the photosynthetic activities of guard cells are very less so this was not accepted very much.
ii) Classical starch hydrolysis theory:- This theory was spelled out by Sayre in 1923 and then modified by steward in 1964. According to this theory guard cells contain starch. during day time when CO2 concentration is low (in the day time because of photosynthesis the CO2 concentration is low) and the pH of the guard cell will increase then enzyme phosphorylase will become active then this enzyme converts the starch present in the guard cells to glucose 1-phosphate. Then glucose 1-phosphate will change into glucose 6-phosphate and latter this molecule after hydrolysis converts into glucose and phosphoric acid.
phosphorylase
Starch + nH3PO4 = n Glucose 1-phosphate
phosphoglucomutase
Glucose 1-phosphate = Glucose 6-phosphate
phosphatase
Glucose 6-phosphate + water = Glucose + H3PO4
Glucose increases osmotic pressure of the guard cells and guard cells will start to absorb water from the adjacent cells and stomata will open. During night time reverse reaction will take place and due to formation of starch the osmotic concentration of guard cells will decrease and guard cells with loss of water will shrink and then closed. But this was not accepted because
i) Glucose is not found in the guard cells at the time of stomatal opening.
ii) The starch and glucose conversion is usually slow reaction but stomatal movements are rapid.
iii) Malate or K+ ion Pump Hypothesis:- This theory was put forward by Steward in 1974. This theory explains that during day time the pH of the guard cell increases due to absorption of H+ ion concentration in the guard cell. CO2 concentration is less due to its assimilation by mesophyll cells. An increase in pH causes the hydrolysis of starch into organic acids.
Starch --- Hexose Phosphate --- Phosphoglyceric acid --- Phosphoenol Pyruvate
Phosphoenol pyruvate is also the intermediate product of respiratory pathway. So with the help of PEP carboxylase the phosphoenol pyruvate will combine with CO2 forms oxalic acid. Latter this organic acid gets changed into malic acid. Malic acid dissociates into malate and H+ ions. H+ ions will pass out from the guard cells with the exchange of K+ ions. These ions and malate ions will increases the osmotic pressure inside the vacuoles of guard cells and as a result water gets absorbed by the guard cells and stomata will open. In the dark reverse reaction taks place and stomata will closed.

Role of K+ ions in Opening and Closing of Stomata
No comments:
Post a Comment