The process of photosynthesis is completed in two main steps - light reaction and dark reaction. Light reaction occurs in the thylakoids of the chloroplast. This phase requires light for chemical reactions therefor, called photochemical phase. Dark reaction occurs in the stroma region of the chloroplast and does not require any light for the reaction to complete. Therefor, it is also called thermochemical phase. Light reaction begins as soon as the light falls on green leaves. It results in the excitation of electrons and facilitates the downhill journey of these electron with the synthesis of ATP molecules. This process is called photophosphorylation. Two photosystems are involved in the light reaction or in the synthesis of ATP molecules. P700 or photosystem I participated in the cyclic photophosphorylation and both photosystem I and photosystem II are associated in a non-cyclic photophosphorylation. The two photosystems are connected with each other by electron transport chain.
Electron transport chain:- It was first described by Hill in 1939. Electron transport chain is a series of electron carriers over which electron pass downhill journey and releasing energy at each step which helps in the synthesis of ATP. Photosynthesis electron transport chain has two main components connected to each other photosystem I and photosystem II. P680 or Photosystem II absorbs light energy and get excited. Excited photosystem transfer electron to the next carrier phaeophytin. after losing the electron photosystem II will become strong oxidant ( who has the ability of taking electron from others is called oxidant). Meanwhile the photolysis of water or splitting of water will provide the electron to the deficient photosystem II ( Photlysis is the splitting of water in the light which results in the release of molecular oxygen during the process). Phaeophytin after accepting electron becomes strong reducing agent ( who is ready to gives extra electrons to others). Then phaeophytin donates its electron to downhill carriers of ETC. At the end plastocyanin will transfer electrons to P700 or photosystem I. P700 will hand over electrons to special chlorophyll molecule X from where electron transfer first to the iron sulphur protein (FeS) and then to the protein ferrodoxin (Fd). The latter can pass electron to the reductase coplex which helps in reducing NADP+ to NADPH. In electron transport chain two main events are involved first the production of ATP and second the release of molecular oxygen into atmosphere.
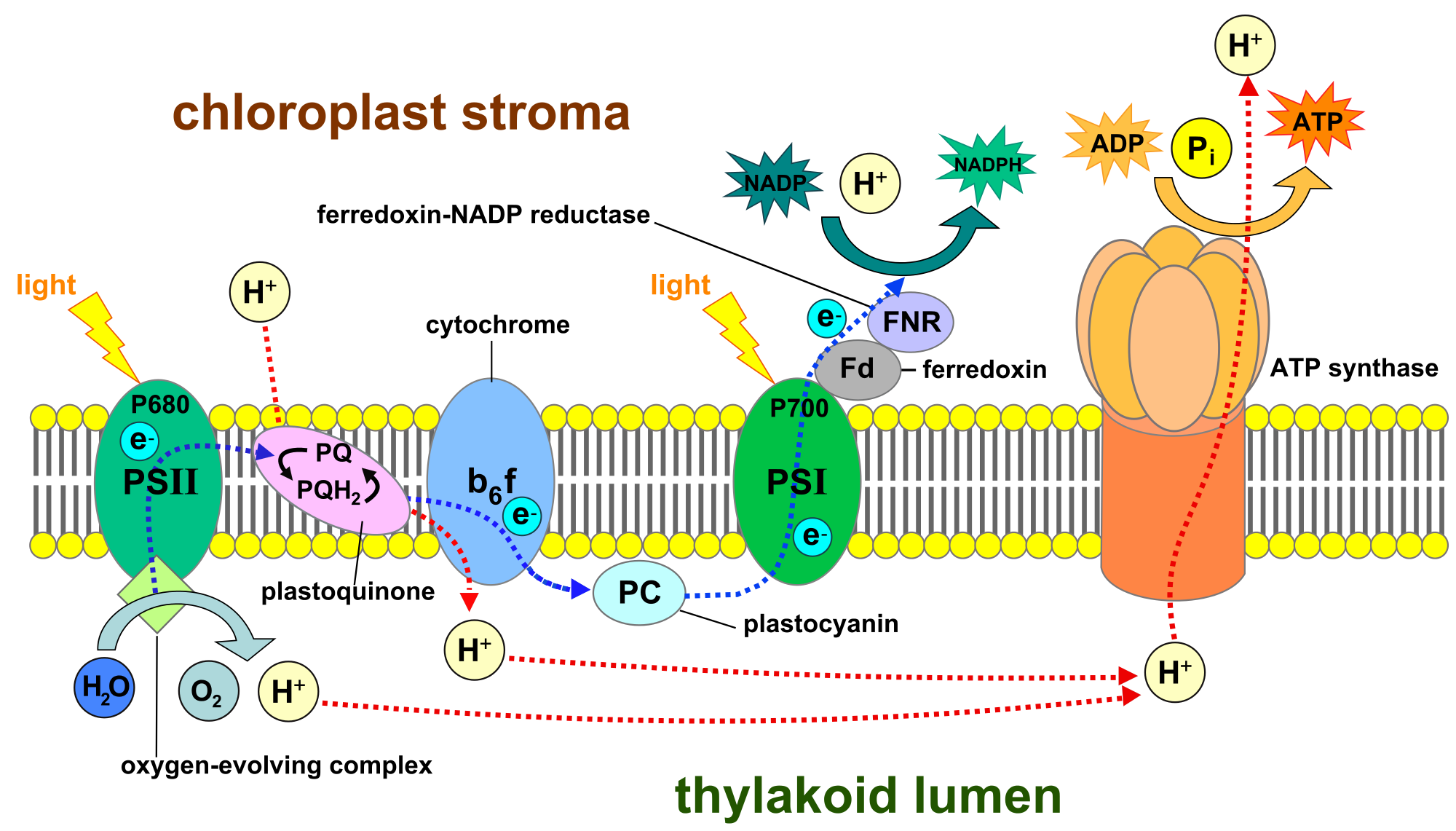
Electron transport pathway in photosynthesis involving two phosystems
Electron transport chain:- It was first described by Hill in 1939. Electron transport chain is a series of electron carriers over which electron pass downhill journey and releasing energy at each step which helps in the synthesis of ATP. Photosynthesis electron transport chain has two main components connected to each other photosystem I and photosystem II. P680 or Photosystem II absorbs light energy and get excited. Excited photosystem transfer electron to the next carrier phaeophytin. after losing the electron photosystem II will become strong oxidant ( who has the ability of taking electron from others is called oxidant). Meanwhile the photolysis of water or splitting of water will provide the electron to the deficient photosystem II ( Photlysis is the splitting of water in the light which results in the release of molecular oxygen during the process). Phaeophytin after accepting electron becomes strong reducing agent ( who is ready to gives extra electrons to others). Then phaeophytin donates its electron to downhill carriers of ETC. At the end plastocyanin will transfer electrons to P700 or photosystem I. P700 will hand over electrons to special chlorophyll molecule X from where electron transfer first to the iron sulphur protein (FeS) and then to the protein ferrodoxin (Fd). The latter can pass electron to the reductase coplex which helps in reducing NADP+ to NADPH. In electron transport chain two main events are involved first the production of ATP and second the release of molecular oxygen into atmosphere.

Electron transport pathway in photosynthesis involving two phosystems
No comments:
Post a Comment