In photosynthesis photophosphorylation is the process in which there is synthesis of ATP from ADP by using the light energy. photophosphorylation was discovered by Arnon et al in 1954. It is of two main types :-
i) Cyclic Photophosphorylation
ii) Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
 Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Cyclic Photophosphorylation

i) Cyclic Photophosphorylation
ii) Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
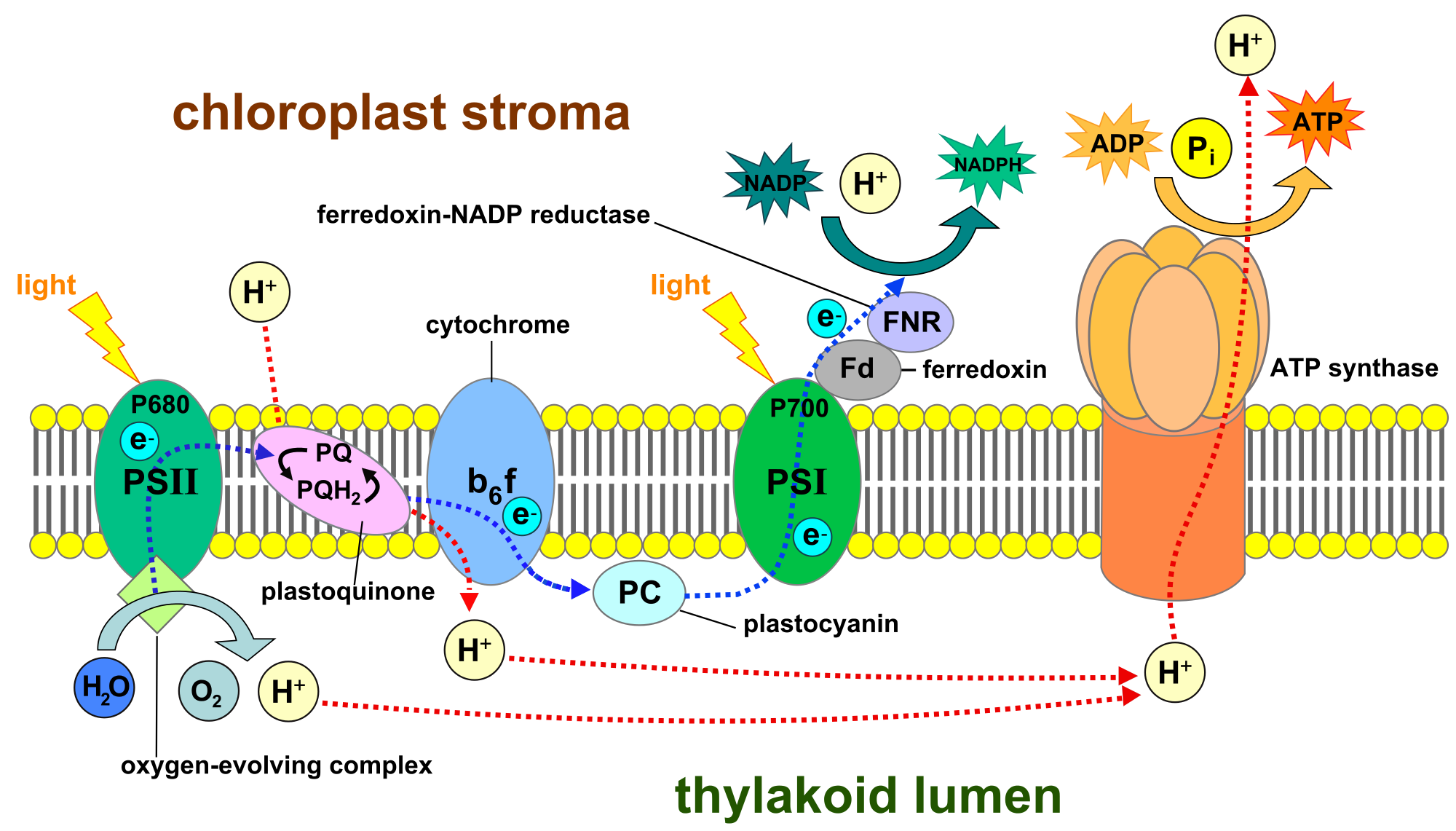
i) Cyclic photophosphorylation:- It is a type of photophosphorylation in which electron expelled from the photocentre returned back to photocentre after passing the downhill journey through series of electron carriers. Cyclic photophosphorylation is performed by photosystem I or P700. Its photocentre extrudes the electron after absorption of light energy ( 23kcal/mole). P700 will become oxidised after losing the electron. The expelled electron will pass through the series of carriers including X then A. FeS proteins ( FeSx, FeSA, FeSB), plastoquinone (PQ), cytochrome b-f complex and to plastocyanin before returning to the photocentre. While passing from carriers electron energises passage of proton to create a proton gradient which actually involved in the synthesis of ATP.
ii) Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation:- It is a type of photophosphorylation in which electron expelled from photocentre does not return to photocentre. Both PS I and PS II participated in non-cyclic photophosphorylation. Photolysis of water will provide the electron to PS II or P680 when PS II is deficienion of electrons. PS II extrudes the electron after absorption of light energy. The extruded electron has an energy equivalent to 23kcal/mole. These electrons passes a series of carriers like Phaeophytin, PQ, cytochrome b-f complex and plastocyanin. While passing from cytochrome complex electron loses energy for the synthesis of ATP. After this electron is handed over to PS I by plastocyanin. Electron again expelled by the PS I after absorption of light energy. The extruded electron passes the journey of electron carries- Chlorophyll X, Fs-S, ferrodoxin to finally reach NADP+. This NADP+ will combine with the H+ ( released from photolysis of water) with the help of NADP reductase to form NADPH.
This is called Z scheme due to zig-zag journey of electrons through the series of electron carriers. The release of molecular oxygen into atmosphere is the result of non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
.PNG)
