The bacteria are unicellular organisms devoid of chlorophyll which reproduce by fission. The name "bacteria" was first used by Ehrenberg (1838) but they were first observed by A.Von. Leeuwenhock (1938) who named them as tiny animalcules.
Occurrence:- Bacteria can grow in all possible environment i.e. in soil, water, in animals and plant bodies. Thermophilic bacteria can live in hot springs.
Shape and form of bacteria:- In shape bacteria cells are of many types. These are
Coccus:- Coccus bacteria are spherical in outline. Depending on their grouping they are (i) Monococcus (occurring singly), (ii) Diplococcus ( in twos), Streptococcus (in chains).
Bacillus:- The bacterium is straight and cylindrical like a rod.
Spirillum:- The bacterium is coiled like a cork-screw.

Occurrence:- Bacteria can grow in all possible environment i.e. in soil, water, in animals and plant bodies. Thermophilic bacteria can live in hot springs.
Shape and form of bacteria:- In shape bacteria cells are of many types. These are
Coccus:- Coccus bacteria are spherical in outline. Depending on their grouping they are (i) Monococcus (occurring singly), (ii) Diplococcus ( in twos), Streptococcus (in chains).
Bacillus:- The bacterium is straight and cylindrical like a rod.
Spirillum:- The bacterium is coiled like a cork-screw.

Vibrio:- The body of bacterium is like a comma, e.g. Vibrio cholerae
Stalked:- The bacterium possesses a stalk, e.g. Caulobacter
Budding:- THe bacterium is swollen at places e,g. Rhodomicrobium.
Flagellation:- On the basis of number and forms of flagella there are following types of bacterial cells.
a) Monotrichous:- Single flagellum at one pole e.g. Vibrio.
b) Amphitrichous:- One flagellum at both the ends. e.g. Pseudomonas.
c) Cephalotrichous:- Two or more flagella at one end only e.g. spirullin midulium.
d) Lophotrichous:- Group of flagella occurs at each of the two ends.e.g. spirilla
Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria:- A Danish scholar Christian Gram (1884) on the basis of staining properties classify bacteria into two groups.
All bacteria turn blue when stained with crystal violet. The bacteria which retain this blue stain after treating with iodine and then with alcohol are called Gram +ve and those which do not retain the blue stain are called Gram -ve.
Gram -ve bacteria are usually pathogenic and more resistant to antibiotics. e.g. E.Coli, Rhizobium Acetobacter, Azotobacter etc.
Gram +ve bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotics. e.g. Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Bacilli etc.
Flagellation:- On the basis of number and forms of flagella there are following types of bacterial cells.
a) Monotrichous:- Single flagellum at one pole e.g. Vibrio.
b) Amphitrichous:- One flagellum at both the ends. e.g. Pseudomonas.
c) Cephalotrichous:- Two or more flagella at one end only e.g. spirullin midulium.
d) Lophotrichous:- Group of flagella occurs at each of the two ends.e.g. spirilla
e) Peritrichous:- A number of flagella are distributed all over the surface. Bacillus. 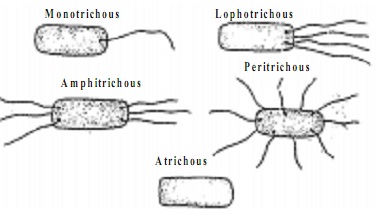
f) Atrichous:- Flagella absent.
Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria:- A Danish scholar Christian Gram (1884) on the basis of staining properties classify bacteria into two groups.
All bacteria turn blue when stained with crystal violet. The bacteria which retain this blue stain after treating with iodine and then with alcohol are called Gram +ve and those which do not retain the blue stain are called Gram -ve.
Gram -ve bacteria are usually pathogenic and more resistant to antibiotics. e.g. E.Coli, Rhizobium Acetobacter, Azotobacter etc.
Gram +ve bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotics. e.g. Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Bacilli etc.
No comments:
Post a Comment